| PAPRIKA OLEORESIN | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
PRODUCT IDENTIFICATION |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| CAS NO. | 68917-78-2, 465-42-9 (Capsanthin), 470-38-2 (Capsorubin) |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| EINECS NO. | 207-364-1(Capsanthin), 207-425-2 (Capsorubin) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
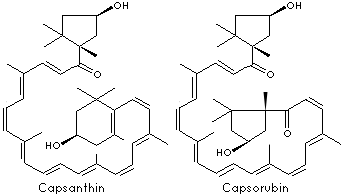
| FORMULA |
C40H56O3, C40H56O | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| MOL WT. |
584.85, 600.85 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
H.S. CODE |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| SMILES |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
TOXICITY |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| CLASSIFICATION |
Natural colorant |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| SYNONYMS |
Capsanthin: (3R,3'S,5'R)-3,3'-dihydroxy-beta,kappa-caroten-6'-one; |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Capsorubin: (3S,3'S,5R,5'R)-3,3'-dihydroxy-kappa, kappa-carotene-6,6'-dione; |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
PHYSICAL AND CHEMICAL PROPERTIES |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| PHYSICAL STATE | reddish oily liquid | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| MELTING POINT | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| BOILING POINT |
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| SPECIFIC GRAVITY |
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| SOLUBILITY IN WATER | Soluble | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| pH | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| VAPOR DENSITY |
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
AUTOIGNITION |
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
NFPA RATINGS |
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
REFRACTIVE INDEX |
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| FLASH POINT |
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| STABILITY |
Stable under ordinary conditions. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
APPLICATIONS |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Paprika Oleoresin, obtained from Capsicum, is a natural dye used as a colorant
and a flavor enhancer in foods, meats and pharmaceuticals. It is obtained by percolation with
a volatile solvent which should be removed subsequently, such as acetone, trichloroethylene, 2-propanol, methanol,
ethanol and hexane. Capsaicin is the major flavouring compound, whereas
capsanthin and capsorubin are major colouring compounds among variety of
coloured compounds present in Paprika Oleoresin.
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| SALES SPECIFICATION | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
APPEARANCE |
reddish oily liquid | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| CONCENTRATION | various | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
SOLVENT RESIDUE |
30ppm max |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| COLOR |
10,000 - 100,000 Color Units |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Capsaicin |
25ppm max |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Arsenic |
3ppm max |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
LEAD |
1ppm max |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
MERCURY |
1ppm max |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
CADMIUM |
1ppm max |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
HEAVY METALS |
20ppm max |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| TRANSPORTATION | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| PACKING | 20kgs
in drum, 200kgs in drum | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| HAZARD CLASS | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| UN NO. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
GENERAL DESCRIPTION OF CAPSAICIN |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Capsaicin is a compound that gives food the hot sensation. It is the most common
of capsaicinoids, followed by dihydrocapsaicin, found in capsicum family of
plants, which rises the heat of chillies. Other capsaicinoids present in the
Capsicum fruit include nordihydro-, homo-, homodihydro-,
nor-, and nornorcapsaicin. Capsaicin is the major flavouring
compound, whereas capsanthin and capsorubin are major colouring compounds among
variety of coloured compounds present in chile peppers. The chemical designation
of capsaicin is N-vanillyl-8-methyl-6-(E)-noneamide. Capsaicin is a lipophilic
white crystalline powder; melting point 60 - 65 C. Capsaicin, as a member of the
vanilloids, desensitizes the sensory nerve endings giving a paradoxical
antinociceptive effect. Capsaicin does not actually cause a chemical burning but
a burning sensation . When nociceptors contact with capsaicin, the neuron is
excited to sign the perception of pain, and there is a local release of
inflammatory mediators. Capsaicin is used in food products to give strong spice
or piquancy. It is used in cream as a paradoxical counterirritant and topical
analgesic ingredient to relieve the pain of peripheral neuropathy. Capsaicin is
also used to dispel insects and animals. It is used as pepper spray or tear gas
similarly. Vanilloids are a group of compounds which are related to capsaicin
structurally. It is known they demonstrate actions via the vanilloid receptor
which is a subgroup of TRP (transient receptor potential) cation channels, very
sensitive to temperature and hot spicy food and capsaicin.
Members of vanilloid include:
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| PRICE INFORMATION | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||